
IARC, Lyon, pp 190–192Įllison DW, Dalton J, Kocak M, Nicholson SL, Fraga C, Neale G, Kenney AM, Brat DJ, Perry A, Yong WH, Taylor RE, Bailey S, Clifford SC, Gilbertson RJ (2011) Medulloblastoma: clinicopathological correlates of SHH, WNT, and non-SHH/WNT molecular subgroups. In: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (eds) WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system, Revised 4th edn. Įberhart CG, Giangaspero F, Ellison DW, Haapasalo H, Pietsch T, Wiestler OD, Pfister S (2016) Medullolastoma, SHH-activated. Ĭoluccia D, Figuereido C, Isik S, Smith C, Rutka JT (2016) Medulloblastoma: tumor biology and relevance to treatment and prognosis paradigm. īihannic L, Ayrault O (2016) Insights into cerebellar development and medulloblastoma.
īartlett F, Kortmann R, Saran F (2013) Medulloblastoma. Īref D, Croul S (2013) Medulloblastoma: recurrence and metastasis. Īrcher TC, Pomeroy SL (2012) Medulloblastoma biology in the post-genomic era. Poor quality of life associated with therapy-related side effects.Īrcher TC, Mahoney EL, Pomeroy SL (2017) Medulloblastoma: molecular classification-based personal therapeutics. Prognosis depends on genetic type, incomplete tumor resection, spread of the tumor. High recurrence rates are noted, even after total resection (40–70%). Treatment consist of surgery followed by chemotherapy and radiotherapy, In this highly malignant tumor 5-year survival rate is about 37%. Several genes known to contribute to chromatin modification have been found to be mutated in medulloblastoma which include the KDM6A gene, EZH2 gene, and SMARCA4 gene (SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4). Group 4 medulloblastoma (>30% ) shows chromosomal aberrations. Group 3 medulloblastoma (~25%) shows enhanced MYC (v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog) amplification and chromosomal aberrations.
Qarc medulloblastoma Activator#
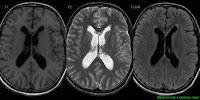
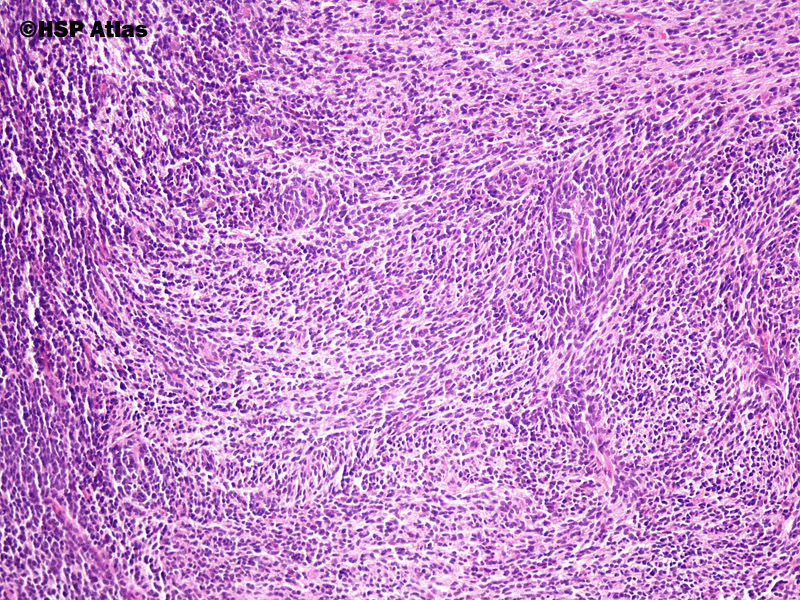
The Shh (Sonic hedgehog) group (~30% of cases) shows germline and somatic mutations in the tumor suppressor gene PTCH1 (encodes the sonic hedgehog receptor patched-1), germline and somatic mutations in the tumor suppressor gene SUFU (encodes the suppressor of fused homolog), amplification of the MYCN oncogene, somatic amplification of the Shh-associated oncogenes GLI1 (chromosome 12q13.2-q13.3 encoding the transcriptional activator GLI family zink finger 1) and GLI2 (chromosome 2q14 encoding the transcriptional activator GLI family zink finger 2), activating somatic mutations in the SMO gene, mutations in DDX3X or KMT2D, and amplification of MYCN. The Wnt (wingless) group (~10% of cases) shows activating somatic mutations in the CTNNB1 gene (encodes β-catenin), germline mutations of the tumor suppressor gene APC (adenomatous polyposis coli), heterozygous mutations in the TP53 tumor suppressor gene, mutations in DDX3X and SMARCA4. Many mitoses and Homer-Wright pseudorosettes are found. Histologically, medulloblastoma is chararcterised by high cell density, cellular polymorphism, densely packed, small, round, carotte-shaped cells with scant cytoplasm, chromatin-rich nucleus. Radiologically, medulloblastoma appears as well-defined, round tumor, typically arising from the roof of the fourth ventricle in older children from the cerebellar hemisphere. It is usually located in posterior cranial fossa and caudal parts of cerebellar vermis.

It affects persons before age 15 and represents 16% of all pediatric brain tumors. Genetically defined medulloblastomas include medulloblastoma, WNT-activated, medulloblastoma, SHH-activated, medulloblastoma, SHH-activated and TP53-mutant, medulloblastoma, SHH-activated and TP53-wildtype, and medulloblastoma, non-WNT/non-SHH.

Histologically defined medulloblastomas include classic medulloblastoma, desmoplastic/nodular medulloblastoma, medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity, and large cell/anaplastic medulloblastoma. Medulloblastoma (WHO grade IV) is an embryonal neuroepithelial tumor arising in the cerebellum or dorsal brain stem, presenting mainly in childhood and consisting of densely packed small round undifferentiated cells with mild to moderate nuclear pleomorphism and a high mitotic count.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
